One of the most common configurations to put in place when we have our website accessible from the internet is redirecting the www URL to an apex domain.
This allows our website to keep its identity and make our brand much more recognizable.
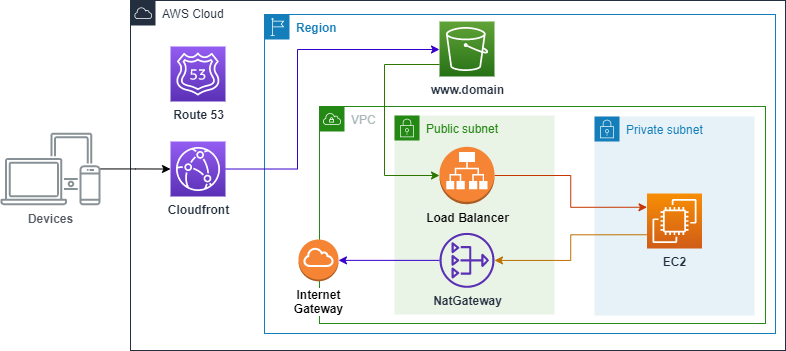
The following diagram represents a typical scenario where we have a Web Server installed in an EC2 instance behind a Load Balancer that redirects the traffic to our server and we will use an S3 Bucket together with Cloudfront to perform the domain redirection.
Repository
As usual, you can find all the Cloudformation templates used to build this example in the GodOfCloud GitHub repository. For this example, the repository only contains a folder with the Cloudformation templates to create the AWS resources.
Requirements
For this example, we have a few requirements that we need to configure before creating all the resources.
- A VPC with at least two public subnets and one private subnet.
- A NatGateway configured in the public subnet because our EC2 will need to have access to the internet to install the Apache server.
- A valid domain in Route 53
- A valid certificate for our domain created in the region where the stack is going to be created, this certificate will be attached to the Application Load Balancer (Only required if we want to configure HTTPS)
- A valid certificate for our domain and *.domain created in the region us-east-1. This certificate will be attached to Cloudfront.
- Copy the template folder from the GitHub repository into an S3 Bucket to be referenced from Cloudformation.
Parameters
prefix:
Type: String
Default: www-redirect-apex
resourcesBucket:
Type: String
vpcId:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC::Id
albSubnets:
Type: List
ec2Subnet:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet::Id
enableHTTPS:
Type: String
Default: true
AllowedValues: [true, false]
albCertificateARN:
Type: String
cfCertificateARN:
Type: String
domain:
Type: StringThe master template has a few parameters that we need to define to configure properly the resources that we are about to create.
- prefix: Prefix name for the resources.
- resourcesBucket: Bucket where all the templates are stored
- vpcId: VPC Id.
- albSubnets: Public subnets where the ALB will be attached (at least two in different availablity zones).
- ec2Subnet: Private subnet where the EC2 Instance will be created.
- enableHTTPS: Flag to enable HTTPS connection (By default is true).
- albCertificateARN: Certificate ARN that will be attached to the Application Load Balancer.
- cfCertificateARN: Certificate ARN that will be attached to Cloudfront.
- domain: Custom domain, for instance, example.com
Solution
To perform the redirection from a domain with www to an apex domain there are three key resources that we need to create
S3 Stack
This stack creates the S3 Bucket that we are going to use to redirect the request from the www domain to the apex domain.
Basically, we configure the S3 Bucket as a Static Website Hosting, with the option of redirecting all the requests to another domain.
Is a good practice to name your Bucket with the full domain name, for example www.example.com, but it’s not really necessary in case the full name is not available.
WWWBucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
BucketName: !Sub 'www.${domain}'
WebsiteConfiguration:
RedirectAllRequestsTo:
HostName: !Ref domain
Protocol: !If [ EnableHTTPS, https, HTTP ]
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration:
BlockPublicAcls: true
BlockPublicPolicy: true
IgnorePublicAcls: true
RestrictPublicBuckets: trueCloudfront Stack
We will configure a Cloudfront distribution to use as origin the S3 Bucket that we’ve created earlier to performs the redirection to our apex domain.
The distribution should have attached a certificate that has the www qualified domain name specified, for instance, www.example.com or a wildcard domain such as *.example.com and define the www.example.com as CNAME.
WWWCloudfront:
Type: AWS::CloudFront::Distribution
Properties:
DistributionConfig:
Comment: Cloudfront distribution for WWW Domain
Aliases:
- !Sub 'www.${domain}'
Origins:
- Id: WWWOrigin
DomainName: !Sub '${wwwBucket}.s3-website.${AWS::Region}.amazonaws.com'
CustomOriginConfig:
OriginProtocolPolicy: http-only
Enabled: true
HttpVersion: 'http2'
PriceClass: PriceClass_All
DefaultCacheBehavior:
AllowedMethods:
- GET
- HEAD
- OPTIONS
Compress: true
TargetOriginId: WWWOrigin
ForwardedValues:
QueryString: false
Cookies:
Forward: none
ViewerProtocolPolicy: allow-all
ViewerCertificate:
AcmCertificateArn: !Ref cfCertificateARN
SslSupportMethod: sni-only
MinimumProtocolVersion: TLSv1.1_2016DNS Stack
The last resource that we need to create is a DNS Record in our Route 53 hosted zone that will relate the domain www.example.com with the Cloudfront distribution.
WWWRecord:
Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet
Properties:
Name: !Sub 'www.${domain}'
HostedZoneId: !Ref domainHostedZone
Type: A
AliasTarget:
HostedZoneId: Z2FDTNDATAQYW2
DNSName: !Ref wwwCloudfrontDomainWhen we create a DNS Record which target is a Cloudfront distribution the Hosted Zone ID is always Z2FDTNDATAQYW2
Deployment
To create all the resources we just need to go to Cloudformation and follow the next steps:
- Select Create Stack → With new Resources (standard)
- Select the option Template is ready
- Specify S3 as a template source
- Paste the URL to the master template in your resources bucket, for example https://my-resources-bucket.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/templates/master.yml
Conclusion
With this simple and cost-effective configuration, we can redirect the typical www to its apex domain.
This configuration is also reversible, therefore with a few modifications in the templates, you could get the opposite, redirect from apex domain to www.
